Understanding the Network Choices That Shape IoT Reliability, Safety, and Performance
As IoT deployments scale across industries — from connected medical devices to smart meters and autonomous vehicles — the security of device communications becomes one of the most important infrastructure decisions an organization must make. At the heart of this decision lies a key question:
Should your IoT devices communicate over the public internet using standard mobile data, or should you deploy a Private APN for controlled, secure connectivity?
Both environments have strengths, but the differences matter — especially when dealing with mission-critical or sensitive data. Understanding how each option works, and the risks and benefits associated with them, will help you choose the right foundation for your IoT ecosystem.
🌐 What Is Public Internet Access for IoT Devices?
When IoT devices use a standard mobile data connection, they operate just like any smartphone or tablet: they connect to the public internet through a mobile network operator’s (MNO’s) infrastructure.
Advantages of Public Internet Access:
- Easy to deploy — no special setup required
- Cost-effective for small or non-critical deployments
- Globally compatible with minimal technical configuration
- Fast to scale for testing or early-stage rollouts
However, because traffic flows through the public internet, devices become more vulnerable to several risks, including:
- Exposure to public IP ranges, which makes them discoverable
- Higher risk of malware, spoofing, SIM hijacking, and DDoS attacks
- Greater dependency on the MNO’s shared network environment, offering less control
- Difficulty enforcing strict firewall or routing policies across fleets
For many consumer IoT deployments this setup can still be appropriate, but for enterprise IoT — especially in industries like healthcare, energy, transportation, and government — public connectivity often introduces unacceptable security gaps.
🛡️ What Is a Private APN?
A Private Access Point Name (Private APN) gives enterprises their own dedicated gateway into a mobile network. Instead of devices connecting to the open internet, they connect to a private, isolated network environment that only your organization controls.
Think of it as a secure tunnel carved inside the mobile network operator’s infrastructure.
How It Works:
- Devices connect using a private APN identifier
- All data routes through segregated gateways, not the public internet
- Traffic can be directed into your corporate network, cloud environment, or VPN
- Devices typically receive private (non-routable) IPs
- Firewalls, routing rules, and access policies become fully customizable
A Private APN is essentially your private network in the cloud, with mobile connectivity as its backbone.
🔒 Security Benefits of Private APN for IoT
When protecting IoT devices from external threats, a Private APN offers multiple layers of hardened security. For mission-critical applications, this can be the difference between stable uptime and catastrophic vulnerability.
1. Devices Become Invisible to the Public Internet
Most cyberattacks begin with network scanning and enumeration.
With a Private APN:
- Devices cannot be scanned
- They cannot be directly reached from outside networks
- Attackers have no entry point to probe
This reduces the threat surface dramatically.
2. Controlled, Encrypted Tunnels (VPN / IPsec / GRE)
Private APNs typically integrate with:
- IPsec tunnels
- Private VPNs
- Cloud interconnects (AWS, Azure, GCP)
This ensures that data travels through secure, encrypted channels from device to backend — never in the open.
3. Custom Firewall, ACL, and Routing Policies
Instead of relying on a mobile carrier’s general-purpose security, you can define:
- Whitelisted IP ranges
- Layer-3 and Layer-7 firewall rules
- Device-to-device communication policies
- Traffic shaping, filtering, and monitoring rules
This level of control is impossible with public internet access.
4. Private Static IPs for Secure Device Management
Private APNs allow each IoT device to receive a private, fixed IP address, enabling:
- Device authentication
- Secure remote management
- Predictable asset routing
- Cloud-based command and control
In contrast, public connectivity typically assigns dynamic, carrier-NATed IPs with limited remote-access options and higher security risks.
5. Better Protection Against SIM-Based Attacks
With a Private APN environment, you can enforce:
- IMEI-locking
- SIM-to-device binding
- Closed-loop routing
- Access limiters (aka IP Filtering)
These policies greatly reduce risks like SIM cloning, SIM swapping, or unauthorized usage.
🏢 Why Enterprises Prefer Private APNs for IoT at Scale
As IoT fleets grow into the thousands or millions of devices, enterprises need to guarantee not only security but also operational control and network predictability.
Private APNs provide:
Centralized oversight and uniform policy enforcement
Security and network rules apply instantly across all devices — no matter where they are located globally.
Higher uptime and stability
Private routes avoid public internet congestion and lower latency variability.
Improved compliance posture
For industries regulated by HIPAA, GDPR, SOC2, or NERC-CIP, private traffic flows simplify compliance by keeping data segmented and auditable.
Seamless integration with corporate IT infrastructure
A Private APN acts like an extension of your internal network — making IoT part of your enterprise architecture rather than an isolated environment.
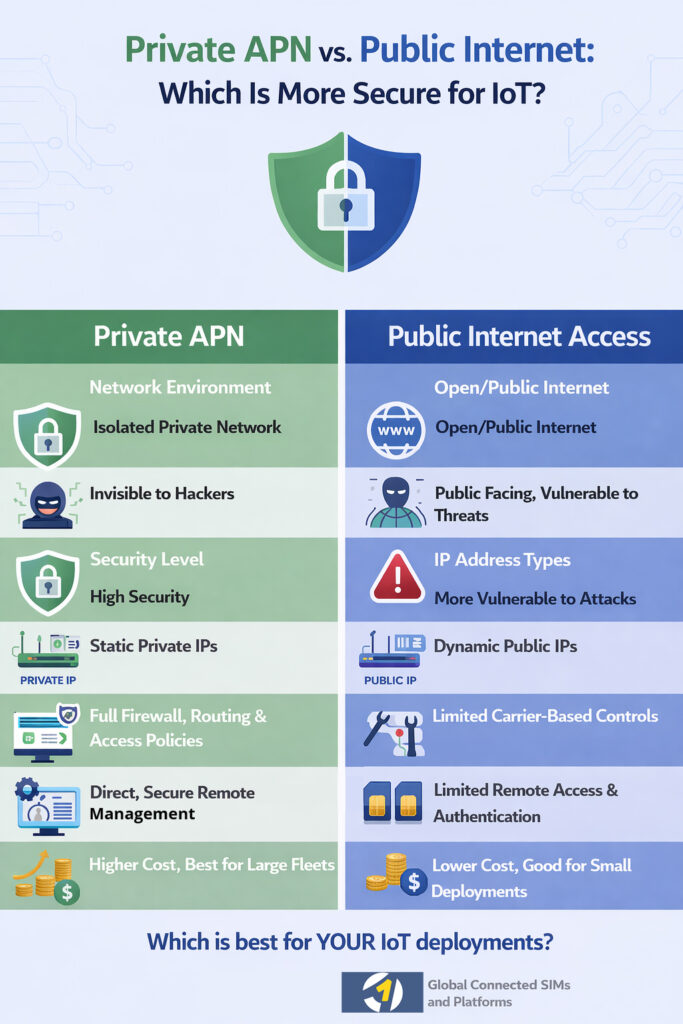
⚖️ Private APN vs. Public Internet for IoT: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Public Internet Access | Private APN |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Moderate (shared network) | High (isolated and private) |
| Device Exposure | Public-facing IPs | Not exposed to internet |
| Management | Limited control | Full policy, routing & firewall control |
| Scalability | Good for small fleets | Best for medium-to-large fleets |
| Compliance | Harder to meet strict standards | Easier to secure & audit |
| Cost | Lower | Higher but justified for enterprise-grade security |
🧭 When Should You Choose a Private APN?
A Private APN is ideal when:
- Devices transmit sensitive data (healthcare, government, finance)
- Uptime is mission-critical (utilities, EV charging, industrial automation)
- Devices run in remote or hostile environments
- You manage hundreds or thousands of IoT endpoints
- Direct device access or remote management is required
- Compliance and audit trails matter
If security, reliability, and centralized control are top priorities, a Private APN will always outperform public internet access.
🚀 The OneSimCard IoT Advantage
OneSimCard IoT provides robust connectivity solutions tailored for enterprise IoT security, including:
- Private APN options with custom IP ranges
- Private static IPs and secure VPN tunnels
- Multi-IMSI global IoT SIM cards for maximum uptime
- Non-steered connectivity to ensure the strongest network at all times
- International coverage across 200+ countries
- Advanced SIM management portal for real-time monitoring and control
With OneSimCard IoT, your devices operate inside a secure, isolated, enterprise-grade environment — ensuring your IoT data stays protected from the first packet to the last.
🔚 Final Thoughts
As IoT continues to shape industries around the world, the network environment you choose will directly impact your security, reliability, and operational costs. Public internet access can work for small-scale or low-risk deployments, but when your IoT infrastructure becomes mission-critical, the benefits of a Private APN become undeniable.
Private APN = security, visibility, and control.
Public Internet = convenience and quick deployment.
For enterprises serious about IoT security, the choice is clear.
